Adios Cassini
A couple of months ago, 15 September to be precise, marked the end of an era in the human exploration of our solar system. The Cassini spacecraft was programmed to crash into Saturn’s upper atmosphere and burn up, thus ending an almost two-decade journey and exploration of Saturn and its moons. I was in middle school when this mission launched in 1997, and at that point, even reaching Saturn in 2004 seemed eons away. Twenty years later, perhaps it’s time to look back at some of the amazing insights we’ve gained.
Cassini is actually a shortened name for the Cassini-Huygens mission, and comprises the main spacecraft — Cassini — designed to travel as a satellite in the Saturn planetary system, and a small lander — Huygens — designed to actually land on Titan, Saturn’s largest moon.
Giovanni Cassini was an Italian mathematician and astronomer, and discovered four of Saturn’s moons — Iapetus, Rhea, Tethys and Dione. The Cassini spacecraft was the first to observe all four of these moons. Christiaan Huygens was, of course, a famous Dutch astronomer and scientist, and discovered — but of course — Titan, then the first known moon of Saturn. (He also invented the pendulum clock, was mentor to Gottfried Leibniz, studied optics and the wave nature of light, and derived the modern formula for centripetal force.)
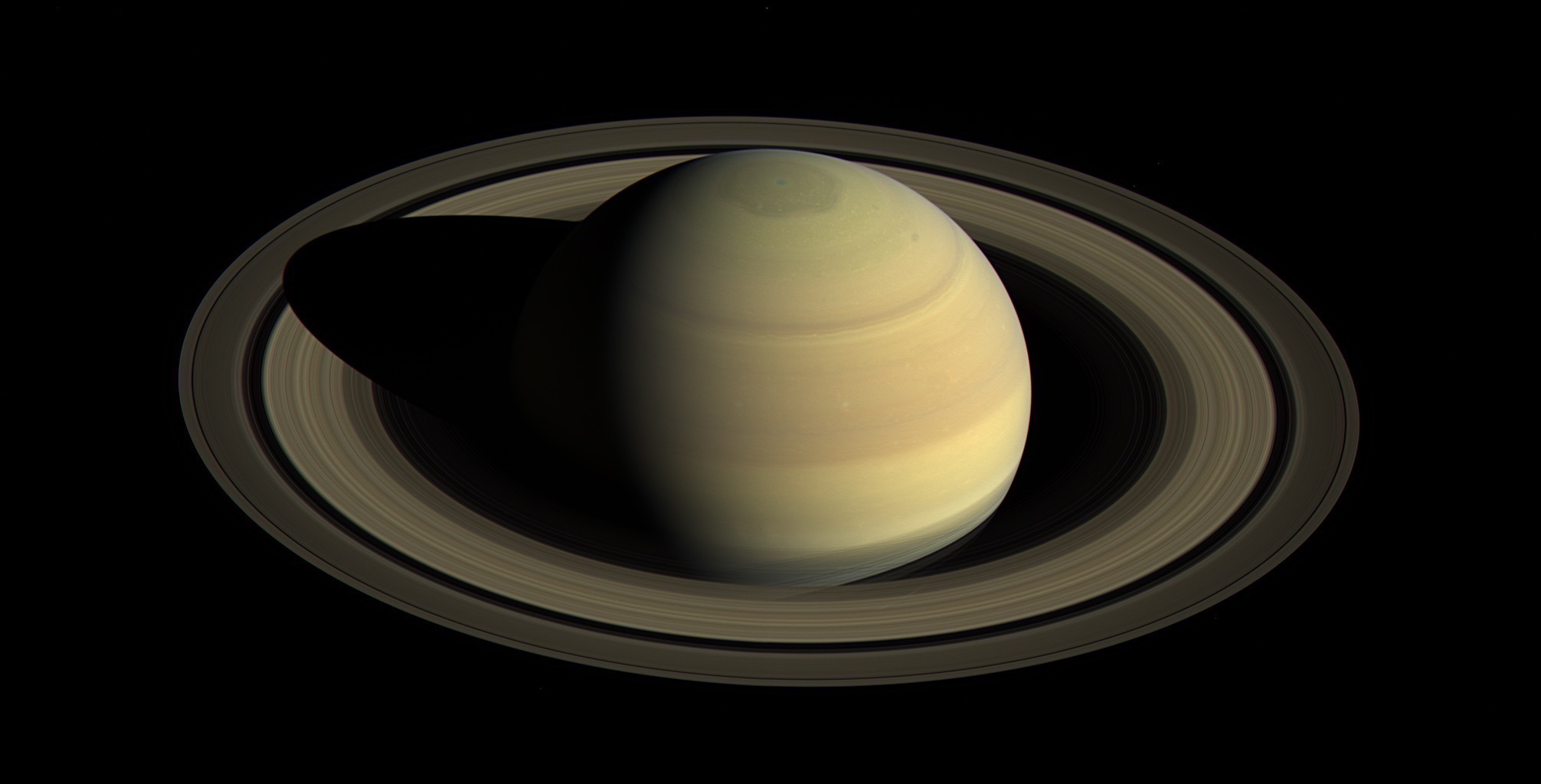

Saturn by Cassini (via Wikipedia).
Of the many discoveries made by Cassini, I’ll focus on just two stories: those of Saturn’s largest moon Titan, and Saturn’s hexagon. Both of these fascinate me to no end, and I think reflect the best of Cassini’s contributions.
Saturn's Polar Hexagon
Jupiter is famous for its Great Red Spot; Saturn has its own atmospheric phenomenon that’s equally fascinating. Saturn’s Hexagon was first discovered by the Voyager missions, but now Cassini has had the chance to see it from up close.
Technically, the Hexagon is a persisting cloud pattern formed by jet streams around Saturn’s north pole, but its sheer size and perfect symmetry make it unique. Each side of the hexagon is about 13800km long (to compare, Earth’s diameter is about 12700km), and its winds travel at around 300km/h. It’s been there since the Voyager missions in the 1980s, so we know its long-lived.
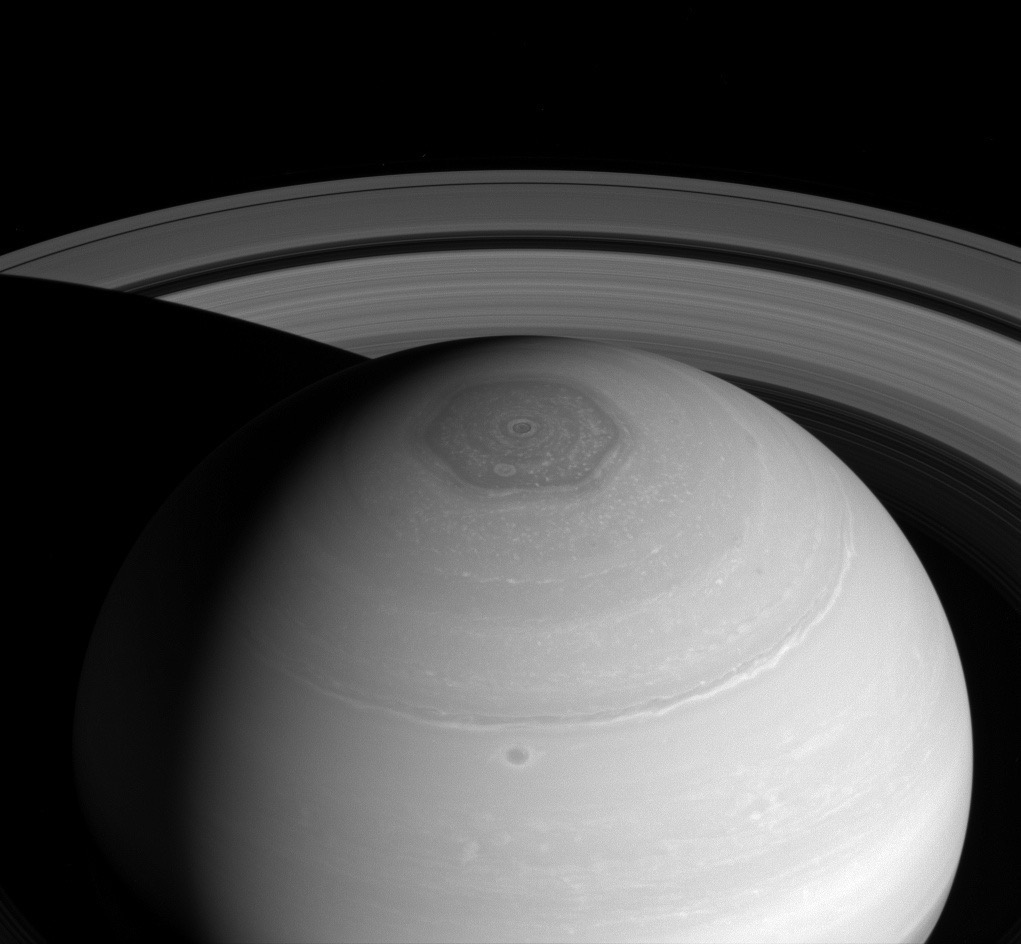

Saturn - North polar hexagon and vortex as well as rings (April 2, 2014) (via Wikipedia).
On Earth, our jet streams are forced to bend and move in response to Earth’s surface features such as mountains. Saturn is much larger than Earth (Saturn diameter is about 116000km) but has a rocky core that’s similar in size to Earth, and so its jet streams have no such problems, and can keep flowing in their own orderly and symmetrical fashion.
The hexagon is essentially a quirk of fluid mechanics. Here on Earth, scientists have been able to create (here, and here) such regular shapes by rotating a circular tank of liquid at different speeds at its center and outer edge. Due to the difference in speeds, a turbulent region is created where such regular shapes can be observed. The regular shape is not always a hexagon (shapes with three to eight sides, i.e. from a triangle to an octagon, are produced) but a hexagon is the most commonly occurring. However, the phenomenon only occurs when the speed differential and fluid properties fall under certain small margins, and therefore the hexagon phenomenon is not observed everywhere where its possible (such as Jupiter, or even the south pole of Saturn).
At the center of the Hexagon, right at the north pole, is a humongous storm, with a definite and easily observed eye wall. The south pole has such a storm as well, although it doesn’t display a Hexagon. In each case, the eye of the storm is about 50 times wider than a hurricane would be on Earth.
As much as the Hexagon is an atmospheric and scientific phenomenon, explained and replicated under lab conditions, it’s one of our solar system’s most beautiful sights, and something I’ll keep looking for in photos of Saturn, now that I know it’s there.
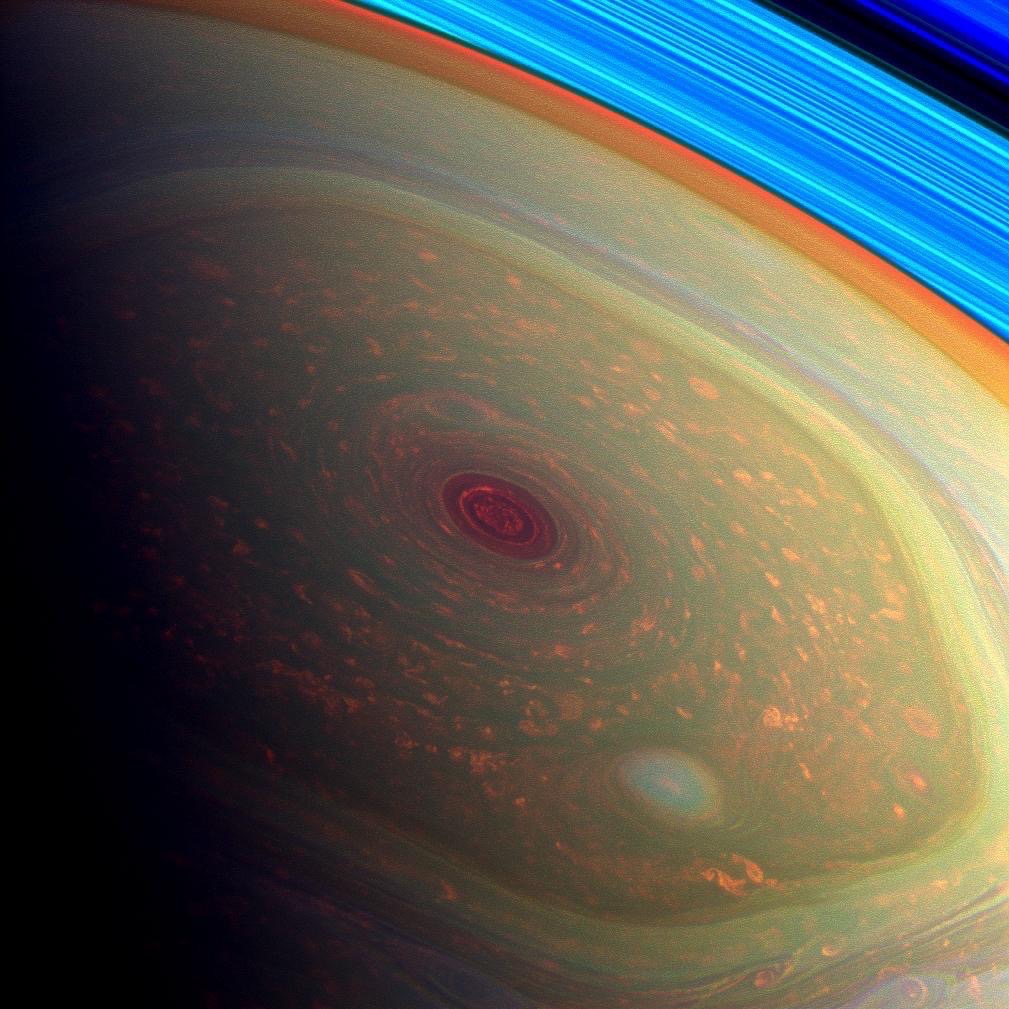
False color image of storms at Saturn’s north pole (via JPL/NASA).
Titan
Titan is Saturn’s largest moon, and of special interest to us: Titan is the only known moon with an atmosphere, and the only one other than Earth whose atmosphere is majority nitrogen. Moreover, its atmosphere is denser and more massive than ours, and is opaque at many wavelengths of light. This means that, like Venus, we had no idea of what the surface of Titan looks like until we had a probe that could land on the surface of Titan. Thanks to Cassini and Huygens, we know a lot more today about Titan than we did in 2004.
Titan, we know now, has an active weather system, including wind and liquid rain, just like on Earth. Of course, the liquid that rains is different from Earth: it rains liquid methane on Titan. Nevertheless, its nitrogen atmosphere and presence of liquids means that Titan’s methane cycle is analogous to Earth’s water cycle. Titan’s upper atmosphere is also affected by ultraviolet light from the Sun, whereby atmospheric methane is broken down and reconstituted into a diverse mix of complex hydrocarbons.
We’re not done yet with the comparisons with Earth! Titan has lakes and oceans, comprised of methane, ethane, and dissolved nitrogen; this makes Titan only the second object in the Solar System (after Earth) to have stable liquids present at ambient temperatures. It most likely also has volcanoes, and is affected by tidal effects from Saturn’s massive gravity. Titan’s surface, specifically where Huygens landed, looks uncannily like Earth, with ‘globules’ about 10-15cm in size, made probably of water ice.

Huygens’ view of Titan’s surface (via Wikipedia).
It’s almost as if Titan is an analogue of Earth— only much colder. In fact, in very specific ways it’s not even colder by much thanks to Titan’s greenhouse effect and tidal heating from Saturn. Cassini has performed numerous gravity measurements of Titan, which reveal that there is a hidden, internal, ocean of liquid water and ammonia beneath Titan’s surface.
So, to summarize, Titan has: an active weather system, large quantities of complex hydrocarbons (Titan is much, much richer in hydrocarbons than Earth), tidal effects from Saturn, and interaction of its atmospheric methane with ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, and even and underground ocean of liquid water and ammonia. A question is begging to be asked at this point: what are the chances of life (past, present or future) on Titan?
Scientists think Titan definitely has the potential to contain habitable environments. Similar to Earth in its infancy, Titan today has the pieces needed for new life to possibly form. Whether it already has, or the extent of future possibility, can only be understood with even better exploration. Indeed, quite a few ideas for future missions dedicated to Titan have been proposed, but none have really gotten off the ground (pun intended) yet.
The most promising of them all is a design to send a submarine to Titan that can explore the seas of Titan, but even this idea is in relatively early stages.
So Much More...
I’ve really just scratched the surface here of how much the Cassini mission gleaned from the Saturn system. There’s so much more: Saturn’s rings and their composition; the moon Enceladus and its jets of icy particles and subsurface ocean of salty water; the moon Iapetus and its equatorial ridge; the moon Mimas and its crater that gives it the Death Star look… trust me, if you don’t take an interest yet, you will once you start reading.
The Cassini-Huygens mission really gave us glimpses into a planetary system that provides great opportunities for scientific discovery, amazing new and diverse worlds, and even — dare we dream? — possibilities of places that can harbor life.
It’s time to say adios to Cassini, but of course, we humans have a long way to go before we can say we know our own solar system.
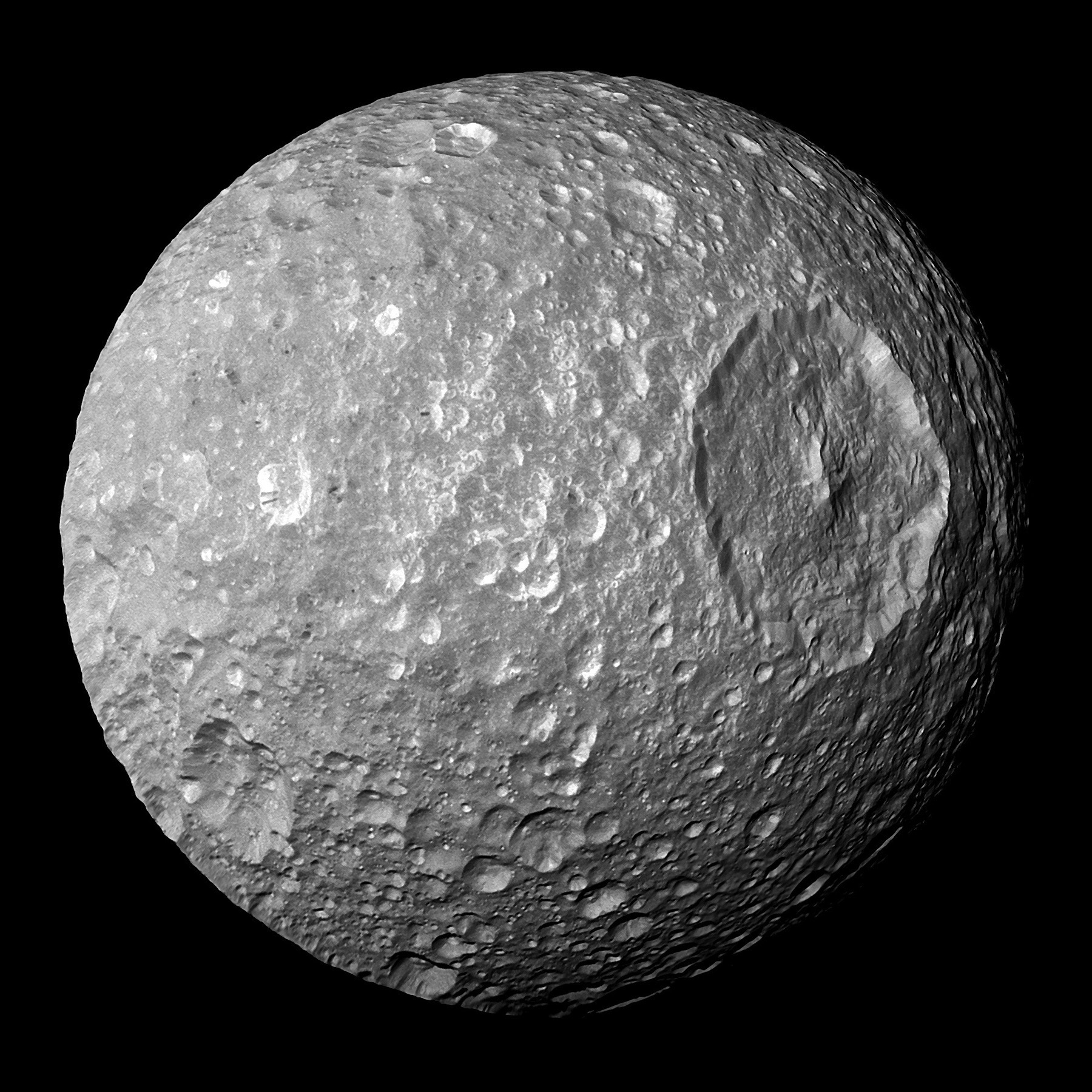

Saturn’s moon Mimas, with the crater Herschel visible prominently (via Wikipedia).
(This piece first appeared in the 2017 edition of Sharod Sombhar, an annual magazine from the Bengali Students’ Association at Virginia Tech.)